The Base ↔ Meesho connection is like getting a single remote control for your entire Meesho store. Instead, it brings everything you do on Meesho—like handling orders, tracking your stock, and managing shipping—together into one along with other marketplaces.
It functions as a synchronization and automation layer, accurately fetching data from Meesho, reflecting it inside Base, and triggering relevant marketplace actions at the right time.
The objective is clear and operationally focused:
- Reduce manual effort
- Prevent stock mismatches
- Speed up order fulfillment
- Ensure sellers never miss time-sensitive events such as COD orders, shipment deadlines, or return movements
Part 1: Step-by-Step Marketplace Integration
1. Adding a New Meesho Integration
The integration setup begins inside Base.
Navigation path:
Integrations → Add integration
From the marketplace list, search for Meesho and select it. This action initializes the marketplace connector that links your Base account with your Meesho seller account.
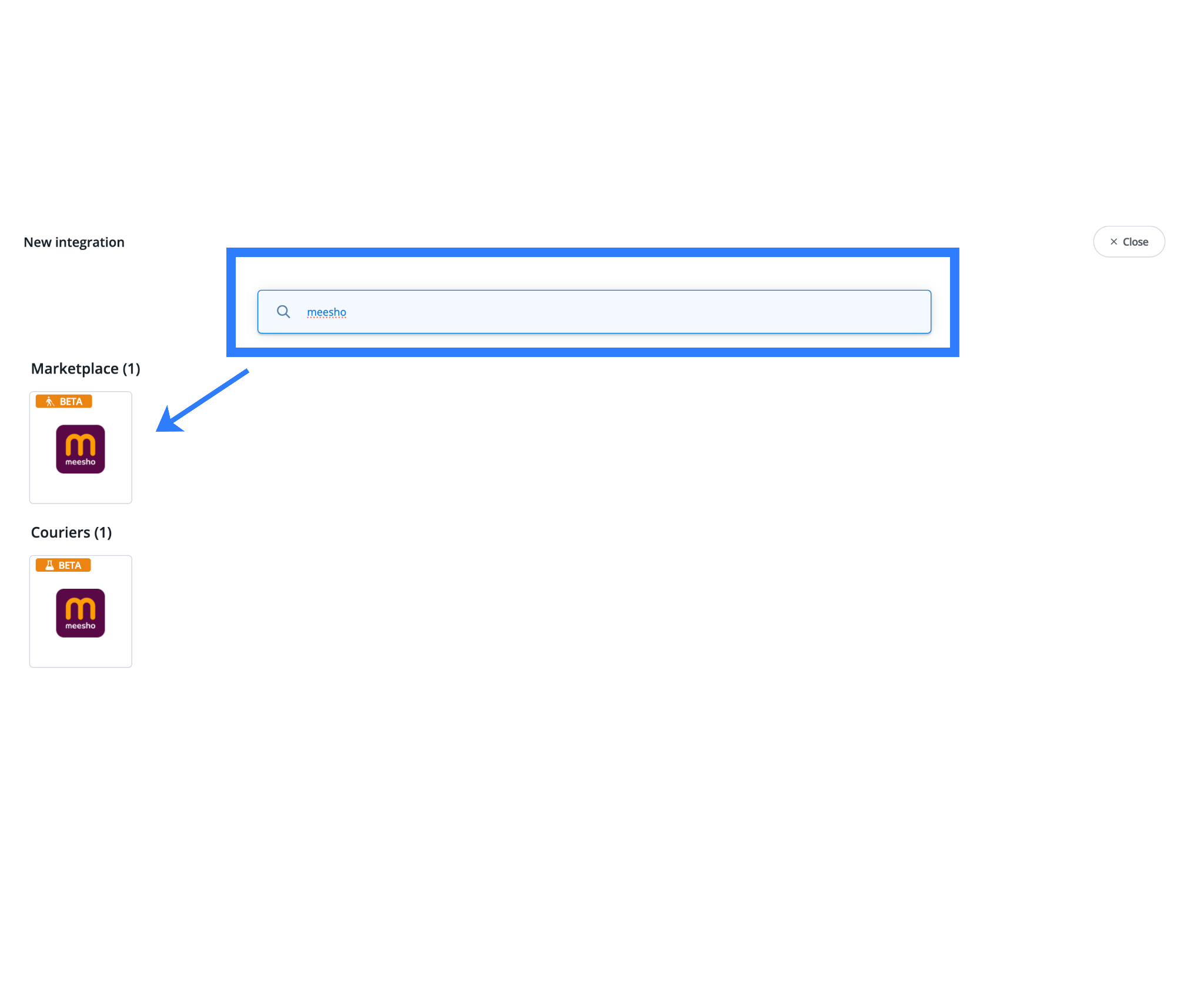
This step establishes the foundation for all downstream processes, including:
- Order synchronization
- Inventory updates
- Catalog imports
- Status and SLA tracking
Without this connector, no marketplace data flows into Base.
2. Entering and Validating Credentials
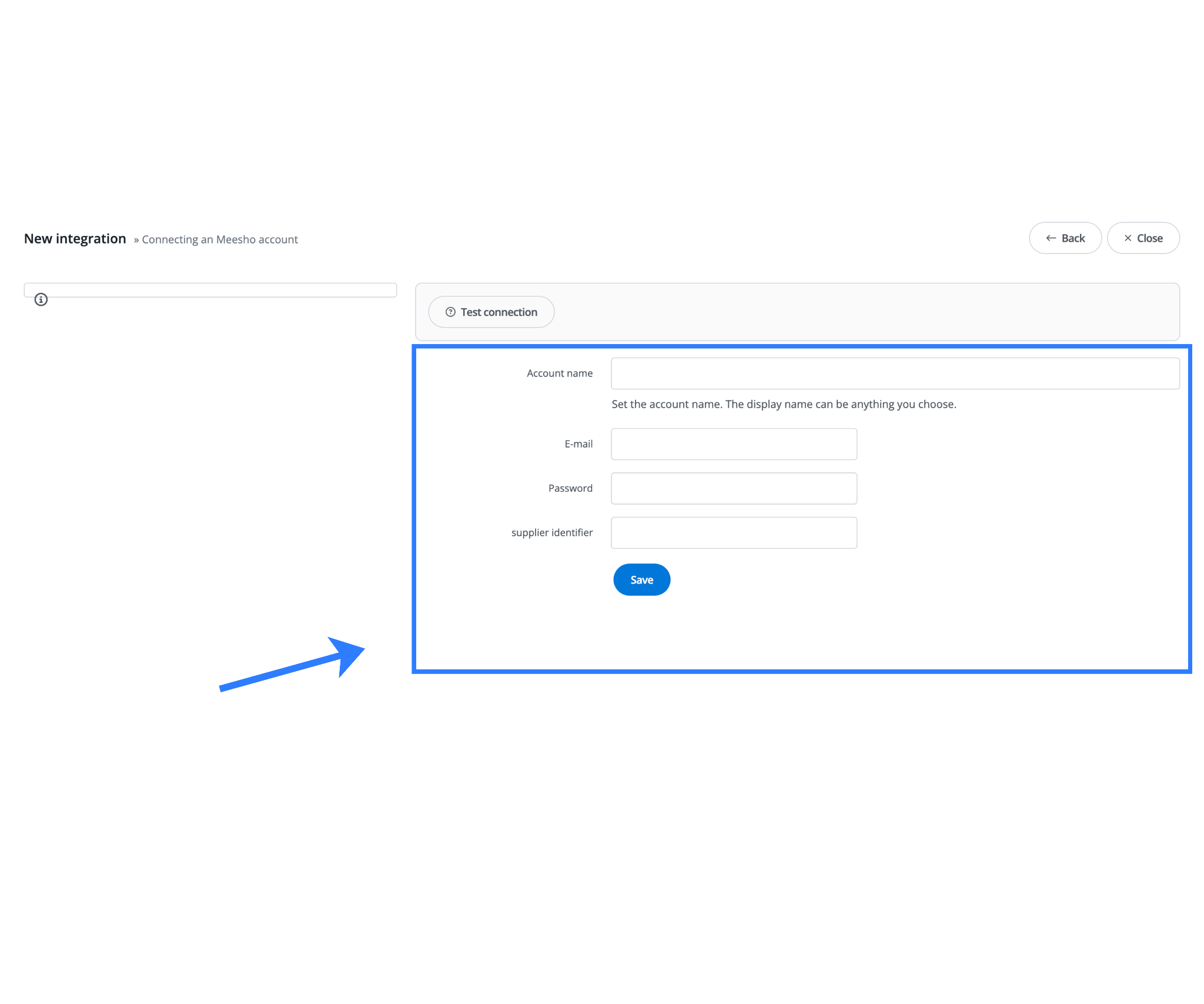
After you select Meesho, the system prompts you to enter the following details:
- Account Name
An internal reference name such as “Meesho Main Store” or “Meesho Wholesale Account”. This is used only for identification inside Base and has no impact on sync logic. - Email and Password
These must exactly match the credentials used to log in to the Meesho Seller Panel.
When you click Save, Base performs a live authentication check by attempting a test login on the Meesho panel.
If authentication is successful:
- Credentials are securely stored within the connector
- The integration activates immediately
- Order, inventory, and catalog sync become eligible to run
If authentication fails:
- The integration remains inactive
- No data is synced
- Errors must be resolved before proceeding
Important Authentication Logic
This integration uses credential-based authentication, not static API keys. As a result:
- Any password change on the Meesho Seller Panel must be updated in Base
- If credentials are outdated, sync failures may occur silently
- This can lead to order delays, stock mismatches, or shipment issues
Operational discipline around credential updates is critical for uninterrupted syncing.
3. Synchronization Configuration
Once credentials are validated, synchronization settings define how often and in which direction data flows between Base and Meesho.
| Setting | Recommended Value | Operational Reason |
| Order download | Every 5 minutes | Prevents missing fast-moving COD orders |
| Stock sync | ON | Avoids overselling across marketplaces |
| Price sync | Optional | Useful during sales or festive pricing |
| GST invoice template | Indian GST Invoice | Auto-calculates CGST, SGST, IGST |
These defaults align with Meesho’s high-velocity order environment and low tolerance for stock errors.
4. Order Status Mapping
Order status mapping aligns Base’s internal workflow with Meesho’s marketplace statuses.
Recommended mappings:
- Packed (Base) → Ready to ship (Meesho)
- Shipped (Base) → Dispatched (Meesho)
This ensures that operational actions taken in Base correctly trigger corresponding state changes on Meesho.
Configuration path:
Orders → Status mapping
Once saved, newly imported Meesho orders begin appearing under:
Orders → Marketplace
Initial orders usually sync within a few minutes of activation.
Core Functional Touch Points
The integration consists of several tightly scoped functional pillars, each designed to operate within Meesho’s rules rather than work against them.
1. Order Synchronization Logic
Order sync is the most critical component.
- Base fetches new and updated Meesho orders at regular intervals
- Only orders in the Pending state are fetched initially
- Each order includes:
- Customer details
- SKU-level item data
- Pricing
- COD or prepaid flag
- Shipment deadlines
Base syncs all marketplace-side changes, such as cancellations or updates, back into the system as soon as it detects them. This ensures Base always reflects the latest marketplace reality.
2. Catalog Synchronization Logic
Catalog sync is designed for visibility and mapping, not marketplace editing.
- Base retrieves active Meesho product listings (offers)
- Sellers can import:
- All offers, or
- Selected offers filtered by SKU
This allows clean SKU mapping between Meesho and Base without duplicating catalogs.
Key principle: Meesho remains the source of truth for product structure. Base mirrors listings only for operational workflows.
3. Inventory Synchronization Logic
Inventory synchronization is push-based from Base to Meesho.
- Any inventory change in Base triggers a stock update to Meesho
- This prevents overselling when the same SKU exists on multiple marketplaces
Because Meesho provides limited inventory buffering flexibility, near-real-time stock updates are essential for accuracy.
4. Order Status Synchronization
Order statuses are synchronized bi-directionally, with defined authority:
- Meesho governs the lifecycle
- Base mirrors the current state
Examples:
- Marketplace cancellations automatically reflect in Base
- Shipment and delivery updates stay aligned across systems
Seller-initiated cancellations are currently not supported and are planned for a future release.
5. Return Synchronization
Returns operate as a distinct workflow.
- Base fetches return orders from Meesho
- Focus is on orders in the IN_TRANSIT return state
Each return record includes:
- Original order reference
- Item details
- Current return status
This enables accurate inbound reconciliation without manual tracking.
Part 2: Meesho Courier Integration
1. Adding the Courier Integration
Navigation path:
Integrations → Add integration → Meesho Shipping
Enter an Account Name and click Save.
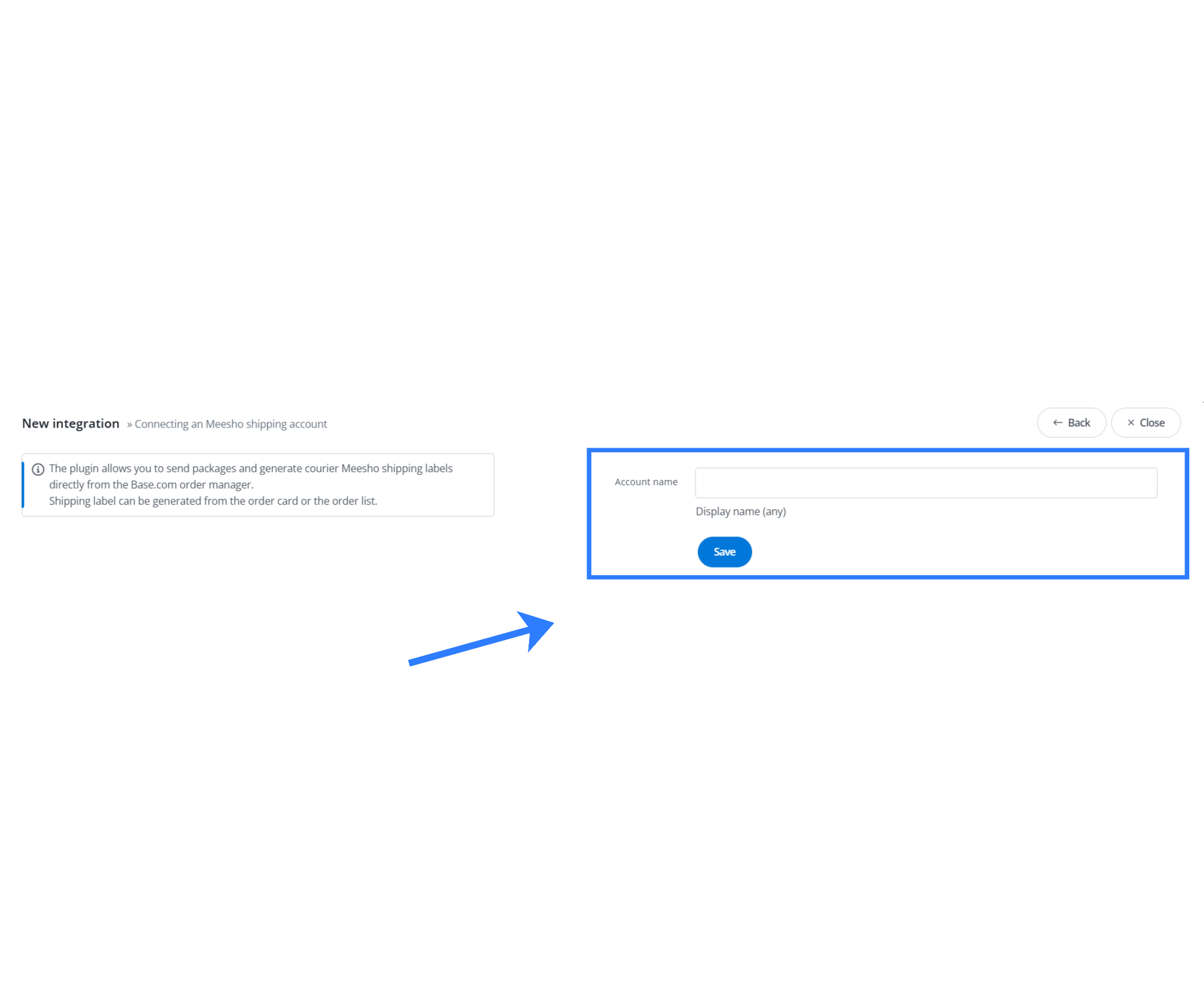
No additional API keys or credentials are required. The courier integration reuses the authenticated marketplace session.
2. Shipment Creation Flow
Once enabled:
- Open any eligible Meesho order
- Click Send package
Base automatically fetches parcel parameters and shipment eligibility. Meesho returns:
- AWB number
- PDF shipping label
No manual data entry is required.
3. Bulk Shipping and Labels
For batch operations:
Orders → Marketplace → Select orders → Ship with Meesho
- Labels and manifests are downloaded as a single ZIP file
- Ideal for sale days or daily dispatch cycles
4. Automation Rules
A commonly used rule:
When order status = Packed → create Meesho shipment + print label
This enables end-to-end automation:
- Orders accepted
- Shipments created
- Labels generated
All without manual intervention.
Final Thoughts
On Meesho, the entire order journey is controlled by the marketplace from start to finish, and the Base ↔ Meesho integration is intentionally designed to work within this structure. An order typically first appears in a Hold state, after which the seller is required to accept it.
Once accepted, Meesho moves the order to the Ready to Ship state, at which point the shipping label becomes available based on marketplace-defined timelines. Meesho then dispatches the shipment using an assigned courier, completes the delivery, and handles any post-delivery states such as completion or return initiation.
Base does not attempt to modify or bypass any part of this lifecycle. Instead, it mirrors each marketplace status accurately inside the system and triggers only those actions that Meesho explicitly allows, ensuring full compliance while simplifying execution for the seller.
The Base ↔ Meesho integration is engineered for operational efficiency within marketplace constraints. It does not attempt to redesign Meesho’s workflows. Instead, it embraces them and removes friction through structured automation, accurate synchronization, and centralized execution.
By combining marketplace and courier integration, sellers gain:
- Faster order processing
- Accurate, real-time stock management
- Zero manual label handling
- Clear visibility into orders and returns
For sellers operating at scale, this integration transforms Meesho from a manual-heavy channel into a rule-driven, fully automated operation managed entirely from Base.
Click here, to integrate AJIO with base.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What happens if my Meesho password is changed after integration is set up?
If you change your password on the Meesho Seller Panel, you must update the same credentials in Base immediately. If not updated, authentication will fail and all sync processes such as order downloads, inventory updates, and shipment creation will stop until the credentials are corrected.
2. Can I manage Meesho shipping couriers or package details from Base?
No. Meesho fully controls courier selection, package dimensions, weight, and shipment timelines. Base does not allow modification of these parameters. It only triggers shipment creation and fetches official Meesho labels, ensuring full compliance with marketplace shipping rules.
3. How often are Meesho orders synced into Base?
“Base fetches Meesho orders at regular intervals—typically every 5 to 10 minutes based on configuration—and initially imports only orders in eligible states such as Pending. The system then automatically syncs any updates, including cancellations or status changes, back into Base.
4. Is it possible to automate order acceptance and label generation?
Yes. Base supports automation rules that can accept Meesho orders immediately upon import and create shipments automatically when orders reach a specific status, such as Packed. This removes manual steps, speeds up fulfillment, and helps sellers consistently meet marketplace SLAs.
5. Does Base support Meesho returns and return tracking?
Yes. Base fetches return orders from Meesho, especially those in the IN_TRANSIT return state. Return records include the original order reference, item details, and current return status, allowing sellers to track inbound returns accurately without manual reconciliation.