
The Indian retail story is being fundamentally rewritten. For years, the narrative was dominated by massive horizontal marketplaces, seemingly unassailable in their scale and discounts. Today, however, a new force is reshaping the landscape: the Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brand. These fast-growing Indian enterprises are not just surviving alongside the giants; they are building superior, highly profitable businesses by deploying advanced technology stacks that empower them with control, efficiency, and a deep understanding of their customer base.
The secret weapon for these D2C champions isn’t just a great product; it’s the strategic integration of a Unified Data Architecture, anchored by robust Order Management Systems (OMS) and precise Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). This tech backbone enables them to move beyond transactional commerce and build long-term relationships, resulting in a customer experience that the largest platforms struggle to replicate.
This deep dive explores the specific, tech-driven strategies fueling the unprecedented growth of Indian D2C brands, demonstrating how they are turning operational challenges into an unshakeable competitive advantage.
How is Owning Customer Data the Ultimate Competitive Advantage for D2C Brands?
The foundational strength of the D2C model is its direct relationship with the customer. By circumventing the traditional middleman, brands gain access to pure, unfiltered first-party data. This data is gold; it provides a 360-degree view of the customer journey, from initial browsing intent to post-purchase feedback, allowing for strategic decisions that marketplaces simply cannot make.
The Precision of Customer-Centric Analytics
Marketplace data is often anonymized and aggregated, offering limited utility. D2C brands, however, capture granular, immediate data from their owned channels, enabling a shift from reactive selling to predictive engagement.
| Data Metric | Strategic Application for Indian D2C Brands | Competitive Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Browsing Intent & Cart Abandonment | Triggers real-time, personalized, geo-targeted offers (e.g., an immediate WhatsApp discount for a Tier 2 customer viewing a high-value item). | Higher conversion rates and maximized session value. |
| Purchase Frequency & AOV | Used to accurately calculate Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), allowing the brand to know precisely how much it can afford to spend on re-engaging a specific segment. | Optimized marketing spend and superior long-term profitability. |
| Regional Preference & Language | Directs the content strategy and informs regional inventory stocking decisions for the WMS, catering to India’s diverse consumer base. | Deeper market penetration and greater perceived relevance in non-metro areas. |
| Post-Purchase Feedback Loops | Provides immediate, qualitative feedback used by product teams for rapid product iteration and quality control improvements. | Superior product-market fit and sustained brand loyalty. |
Hyper-Personalization: Building Loyalty at Scale
In India’s highly competitive e-commerce landscape, personalization is no longer optional; it is a survival mechanism. D2C brands leverage AI and Machine Learning (ML) engines integrated into their storefronts (built on platforms like Shopify Plus or custom systems) to create a tailored experience for every visitor:
- Dynamic Site Content: The website’s banners, product recommendations, and even navigation layouts change based on the customer’s browsing history, demographics, and stage in the purchase funnel. A returning loyal customer might see a preview of an exclusive new collection, while a first-time visitor sees trial packs.

- Virtual and Augmented Reality (AR): Especially prevalent in fashion, beauty, and eyewear, AR allows customers to virtually “try on” products using their phone camera. This reduces purchase hesitation and, crucially, minimizes the high return rates associated with sizing and aesthetic mismatches.
- Conversational Commerce: D2C brands are excelling in WhatsApp and other chat platforms. AI-powered bots handle the routine queries, while sophisticated routing ensures a human agent steps in for complex questions, simulating the experience of a dedicated personal shopper at massive scale.
This personalized customer journey is an unassailable advantage, transforming a simple transaction into a brand experience, which in turn fosters powerful, durable loyalty.
How Do Integrated Order and Warehouse Management Systems Accelerate Scalability?
While personalization wins the customer, the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of the backend operations ensure they keep coming back. This is where the integration of the Order Management System (OMS) and Warehouse Management System (WMS) becomes the true operational backbone, defining the brand’s ability to scale without friction.
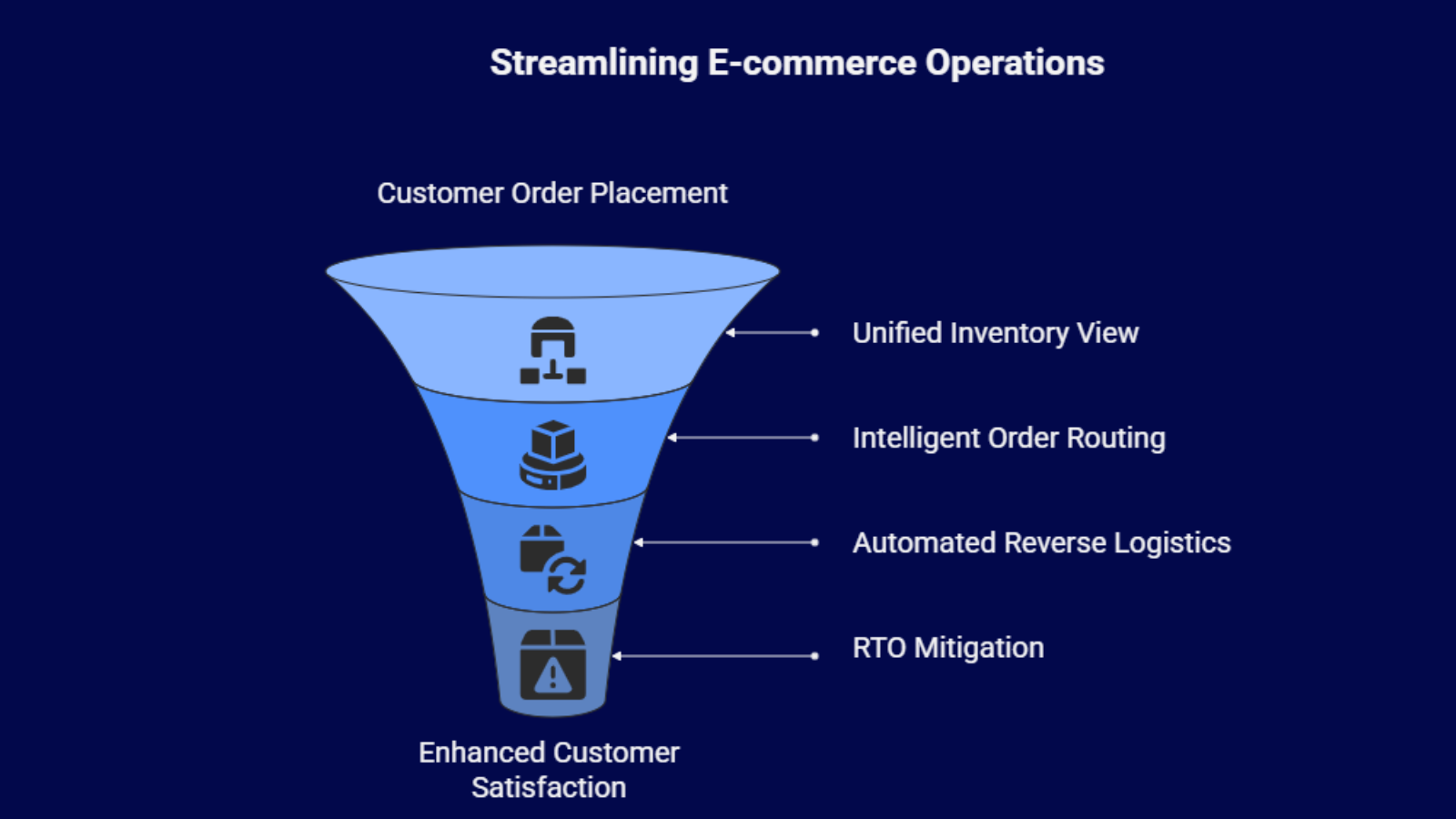
The Order Management System (OMS): The Control and Orchestration Layer
The OMS is the central nervous system of the D2C ecosystem. It integrates all digital sales channels, physical retail points, and the logistics network into a single, cohesive workflow.
- Unified Inventory View (Single Source of Truth): The OMS provides a real-time, consolidated picture of all inventory across the entire network company-owned warehouses, 3PL facilities, dark stores, and even in-store stock. This is essential to prevent costly overselling during peak events.
- Intelligent Order Routing: This is the most crucial function for competing on delivery speed. The OMS uses pre-defined algorithms to instantly route an incoming order to the most optimal fulfillment node. The decision factors include the center closest to the customer, the cost-effectiveness of the available carrier, and the inventory level of the required item. This precision reduces delivery time and lowers shipping costs simultaneously.
- Automated Reverse Logistics: Dealing with returns is a major cost center in Indian e-commerce. The OMS automates the entire process, from generating a return label and scheduling the pickup to initiating a refund or exchange after the WMS confirms the item’s return and quality check. This fast, transparent process is a huge trust magnet.
- RTO (Return-to-Origin) Mitigation: High RTO rates, particularly for COD orders, directly erode margins. The OMS integrates pre-dispatch verification tools (SMS, IVR, or app prompts) to re-confirm COD orders, significantly minimizing the risk of failed deliveries and associated logistics costs.
The Warehouse Management System (WMS): Operational Excellence
The WMS takes the instructions from the OMS and maximizes the efficiency of the physical supply chain. It dictates the movement of people and products within the warehouse itself.
| WMS Function | Operational Benefit | Direct Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| System-Directed Picking Logic | Uses algorithms to determine the shortest and most efficient path for warehouse associates to pick items, often using handheld devices. | Cuts the time taken to fulfill an order, allowing the brand to meet demanding next-day delivery SLAs. |
| Mandatory Scan-Based Verification | Requires barcode scanning at every major checkpoint (receiving, picking, packing). | Drives near-perfect order accuracy, virtually eliminating the costly and damaging error of shipping the wrong product. |
| Batch and Expiry Tracking (FEFO) | Enforces ‘First-Expired, First-Out’ (FEFO) rules for FMCG and consumable goods. | Ensures freshness and regulatory compliance, minimizing inventory spoilage and building consumer trust in product quality. |
| Dynamic Slotting and Putaway | Optimizes the storage location of products based on sales velocity and size, ensuring frequently picked items are easiest to access. | Maximizes the use of expensive warehouse space and reduces labor time. |
What Strategic Role Does Distributed Logistics Play in Market Penetration?
Indian D2C brands cannot rely on the centralized, volume-driven logistics model of their marketplace competitors. To compete effectively, they are building smarter, faster, and more decentralized fulfillment networks known as Distributed Logistics.
Leveraging Micro-Fulfillment Centers and 3PLs
The strategy involves establishing a network of smaller fulfillment centers, dark stores, and leveraging specialized 3PL partners geographically closer to high-density customer zones, particularly in growing Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Proximity-Based Speed: By stocking inventory nearer to the customer, the transit time, the longest variable in the delivery cycle, is drastically reduced. This allows for reliable 1-day delivery in major metros and significantly faster services across secondary markets.
- Multi-Carrier Intelligence: D2C brands utilize tech platforms that aggregate multiple courier partners. The OMS, informed by this aggregation layer, can select the optimal carrier for a specific pin code based on real-time performance, reliability, and cost. This flexibility provides a superior experience compared to being limited to a single carrier network.
- Phygital Fulfillment: The most advanced D2C brands use their brick-and-mortar stores (where they exist) as micro-fulfillment centers. The OMS directs online orders to the nearest retail location for same-day delivery or customer pickup, efficiently utilizing existing real estate to enhance speed and service.
The Branded Last-Mile Experience
For a D2C brand, the final delivery moment is a crucial opportunity for brand storytelling, a touchpoint fully controlled and executed through the integration of the OMS and WMS.
- Premium Unboxing: Unlike generic marketplace packaging, D2C brands ensure their WMS protocols include branded, premium, and often sustainable packaging.
- Personalized Inserts: The WMS instructs the packer to include a personalized message or a targeted discount voucher for a related product, leveraging the customer data pulled from the OMS. This transforms a logistical step into a targeted marketing exercise that encourages repeat purchase.
- Transparent Tracking: Post-purchase experience platforms integrate with the OMS to provide customers with a fully branded, real-time tracking page, unifying tracking information across disparate carriers and drastically reducing customer support queries.
How is AI Redefining the Future of D2C Profitability and Scaling?
The next wave of D2C success in India is being driven by Artificial Intelligence, moving from simple automation to deep intelligence that underpins strategic decision-making and protects margins.
AI-Driven Decision Support
- Predictive Demand Forecasting: AI and ML models analyze historical sales, live website traffic, social sentiment, competitor price points, and even weather patterns to predict future demand with unprecedented accuracy. This intelligence guides inventory allocation for the WMS and purchasing decisions, minimizing costly overstocking and preventing lost revenue from stockouts.
- Dynamic Pricing and Margin Protection: AI tools allow brands to instantly adjust pricing and promotional offers based on customer segmentation (CLTV, price sensitivity) and real-time inventory levels. This allows the brand to maintain a competitive edge without sacrificing margin, making discounts strategic rather than reactive.
- Marketing Attribution and Budget Optimization: AI algorithms provide sophisticated insights into which marketing channels from Instagram to paid search are truly driving high CLTV customers. This allows the brand to allocate its marketing budget with precision, lowering the effective Customer Acquisition Cost over time.
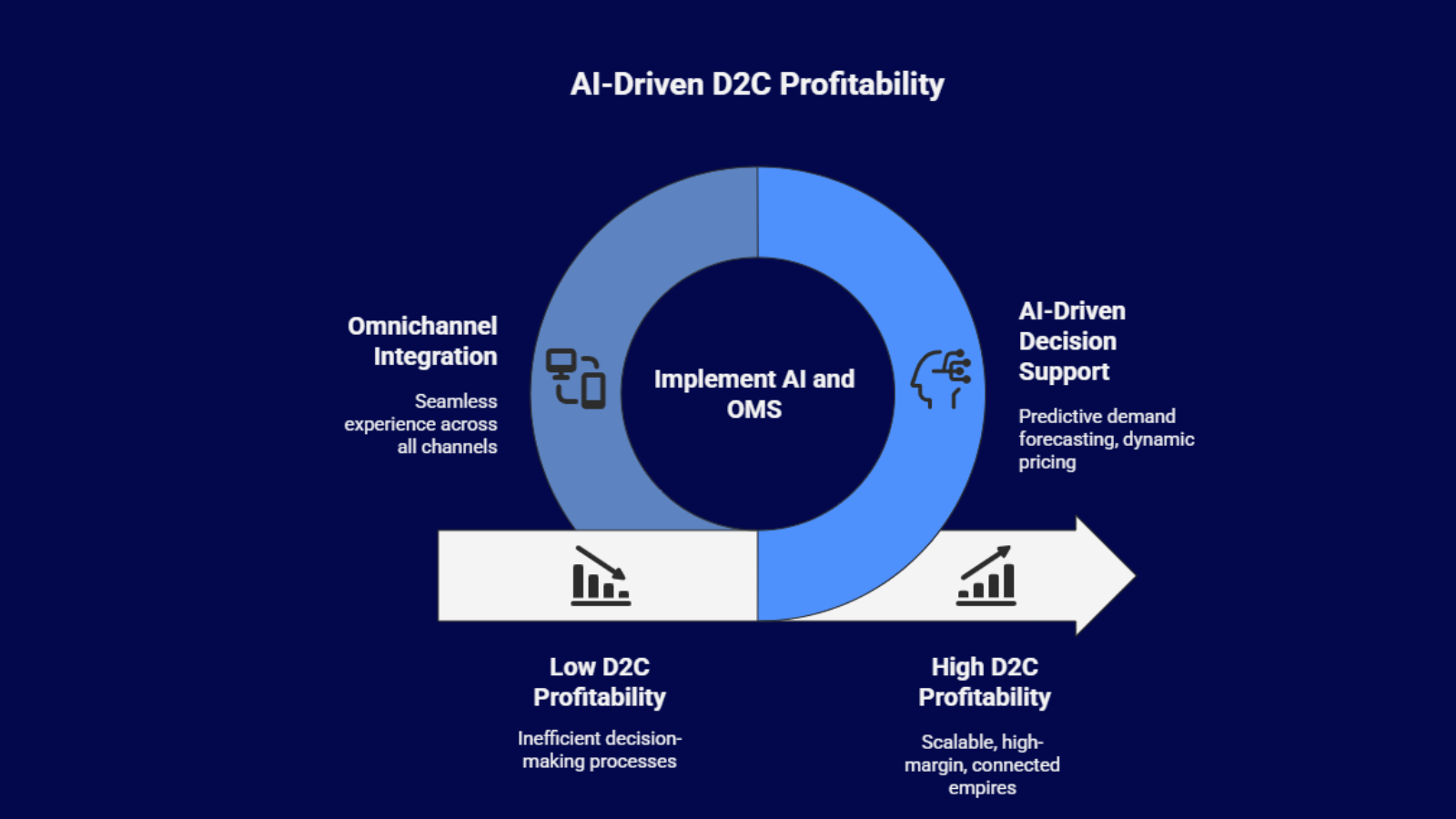
The Omnichannel Integration Mandate
The ultimate winning model for the Indian D2C space is the seamless integration of all channels online, offline, and marketplaces powered by the core tech stack. This ensures a consistent, high-quality, and highly profitable experience regardless of the point of purchase. The key is using the OMS to act as the central ledger, ensuring that all inventory, order history, and customer interactions are consolidated for a singular, coherent brand view.
By moving beyond simple websites and investing in this integrated technology the OMS for orchestration, the WMS for fulfillment efficiency, and AI for predictive intelligence Indian D2C brands are not merely keeping pace; they are setting a new standard for retail excellence, building scalable, high-margin empires that are deeply connected to the consumer.
Ready to gain end-to-end control and scale your D2C operations with a powerful, integrated tech stack?
Explore the future of D2C fulfillment today at Base.com and focus on what truly matters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is it still viable for D2C brands to launch solely on their own website in India?
A. While launching exclusively on a dedicated website provides immediate control over data and branding, most successful Indian D2C brands adopt a blended approach. They utilize marketplaces for initial visibility and high-volume customer acquisition, while actively migrating those customers to their owned website to leverage the higher profitability and data ownership that the D2C channel provides.
Q2. How does the WMS help D2C brands manage the diverse inventory requirements of different categories?
A. Modern WMS solutions use advanced logic that is category-agnostic. For instance, they apply FEFO (First-Expired, First-Out) rules for FMCG and consumables, batch tracking for beauty products, and serialized inventory tracking for electronics. This level of granular control, dictated by the WMS, ensures every product category adheres to its specific quality and compliance standards, something essential in the multi-category D2C space.
Q3. What is ‘Phygital Fulfillment’ and why is it important for scaling D2C brands?
A. ‘Phygital Fulfillment’ refers to the strategy of seamlessly blending physical and digital assets for fulfillment. It’s important because it allows D2C brands to use their existing or new physical retail stores as micro-fulfillment centers. By connecting the store inventory to the central OMS, the brand can offer extremely fast services like same-day delivery or ‘Buy Online, Pick Up In Store,’ leveraging existing real estate to enhance logistical speed and scale.
Q4. How do D2C brands maintain high brand consistency across multiple external marketplaces?
A. Consistency is maintained through the centralized OMS and a strict brand governance strategy. While the marketplace controls the page template, the OMS ensures that product data (descriptions, images, pricing) is unified and pushed consistently across all external channels, preventing discrepancies. Furthermore, by directing customer service and post-purchase communication back to owned channels, the D2C brand retains ultimate control over the experience and narrative.

